
Introduction: E Ink displays, pioneered at MIT in the 1990s and currently owned by E Ink Corporation, power renowned e-readers such as the Amazon Kindle.
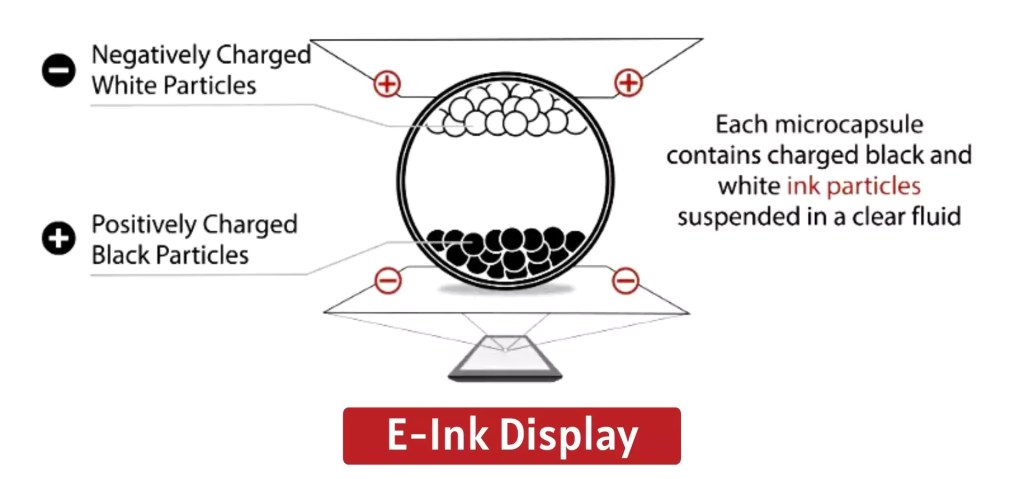
How E Ink Works: The technology operates through microcapsules filled with charged particles, creating text and images by manipulating electrical charges. Unlike LCDs and LEDs, E Ink reflects light like paper, reducing eye strain and offering better readability for extended reading sessions.
Advantages of E Ink:
- Low Power Consumption: E Ink consumes minimal power, only drawing energy when the image changes, resulting in extended battery life for devices.
- Eye-Friendly: The lack of a backlight reduces eye strain, making it comfortable for users during prolonged reading.
- Outdoor Readability: E Ink displays excel in bright lighting conditions, unlike LCDs that may suffer from reduced legibility in sunlight.
Limitations of E Ink:
- Slow Refresh Rate: E Ink’s slower refresh rate limits its suitability for video or animated content.
- Color and Resolution: Compared to other display technologies, E Ink has limitations in color and resolution.
- Cost: Manufacturing E Ink displays, especially in larger sizes, remains relatively expensive.
Applications Beyond E-Readers: While initially popularized by e-readers, E Ink displays are finding applications in bus stop displays, walking direction signs, and restaurant menu boards.
Conclusion: E Ink continues to play a vital role in specific niches, providing unique advantages such as outdoor visibility, reduced eye strain, and extended battery life. As technology evolves, E Ink’s applications may diversify further, leveraging its distinctive features for various purposes.